|
Institutionen för geovetenskaper Geoinformatiklaboratoriet |
GIS Exercise 17 September 1999 |
Thomas
Gumbricht Patrik
Stenberg |
DATA MINING ON INTERNET
|
Requirements The exercise requires a PC with Windows95/98 or Windows NT, a
connection to the Internet and the freeware ArcExplorer 1.1. To install
ArcExplorer from the Internet see appendix 1. The necessary data is mined
from the Internet. |
|
Objectives The objective of the exercise is that the students should gain
insight into using the www as a source of data and exploration tools for
georeferenced data; to introduce some basic elements of digital cartography
including scale, georeferencing, labelling and layout. After completing the
exercise students should be able to create thematic maps from tools and data
available over the www. The first half of the exercise is exactly like the
exercise “Introduction to digital cartography” whereas the second part
(starting at the heading “Add cities over your
selected country”) introduces more advances data mining. |
Task
The exercise aims is to introduce freely available GIS software and georeferenced data over the world wide web (www). As you will use global data sets you could choose to work with any region of the globe. However, the idea is to work with some country/countries in Africa to illustrate typical data for developing regions. The instructions are written for Botswana – a land locked country in Southern Africa. To pass the exercise a thematic map over Botswana must be handed in. |
Start
the GIS Viewing program and add data from internet
In this exercise we will use ArcExplorer ![]() - a
GIS freeware offered by ESRI – see appendix for instructions on how to retrieve
ArcExplorer from the internet.
- a
GIS freeware offered by ESRI – see appendix for instructions on how to retrieve
ArcExplorer from the internet.
|
If you are doing the exercise at home
you will need to download Arc Explorer, (see Appendix). If you are sitting at
Geocentrum you will find ArcExplorer under “Start\Program files\Esri\ArcExplorer1.1”. Start ArcExplorer. |
|
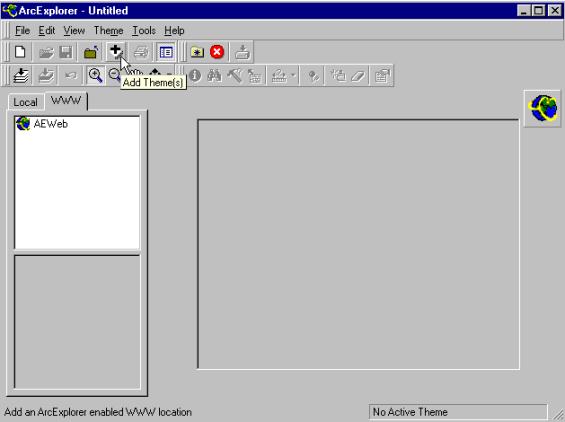
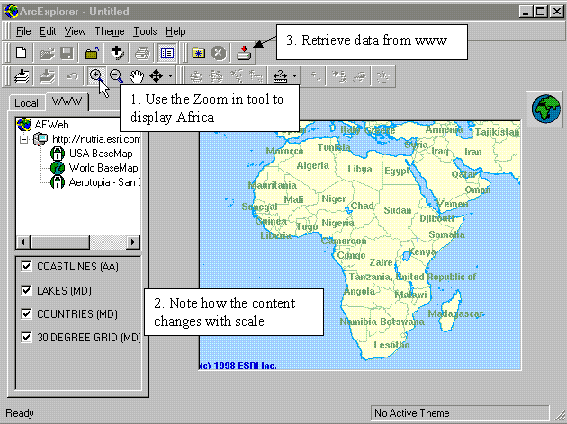
The main parts of the ArcExplorer interface are shown in the figure
below. You will be presented with an empty project called untitled. The legend window contains
two tabs (pages), one for local themes (themes that are stored on your local
computer or local area network) and one for WWW themes (themes stored on Web
sites). To get help on any topic just press F1, or search via help in the menu
bar. You can also find the document Using ArcExplorer (Arcexplorer.pdf) in the same folder as
the program file. This manual can be read by using Adobe Acrobat reader (see appendix
for download of Adobe Acrobat).
In the interface you will notice that some menu and
tool items are gray (fuzzy) that means that they are not available at the
moment. Many items require that you have some themes in the view, (a theme is a
maplayer in GIS jargong) and some that you have at least one theme active (this
will soon be clear to you).
|
Menu bar Tool bars Legend Map View |
|
We will start by adding some maps directly from www.
Choose the www tab from the top of the legend, where after the legend should
look like the one in the figure above. Press the Add theme
button, |
|
|
The legend window
should now have some more items, as shown to the right. Click on “World
BaseMap”. The transfer might take a while but you will then get a view of the
whole globe, with labels for the continents. If you do not get a map the most
likely problem is that you do not have permission to alter the contents in
the archive where you have ArcExplorer i.e. the archive \Esri\ - contact your system administrator (see appendix). Select Data
Use the Zoom in tool, Also try the pan tools |
|
|
|
|
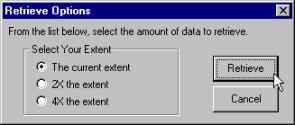
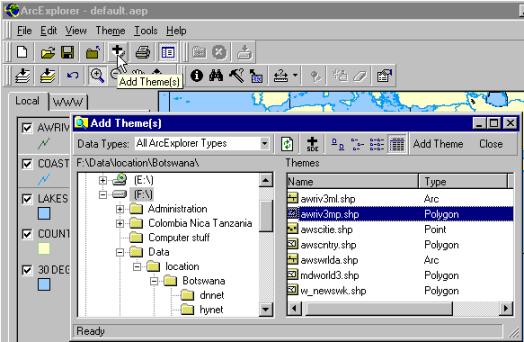
2. Press open button to retrieve data from the www to your
selected or created folder |
1. Create new folder
|
Answer Yes to the question “Would you like to add the
data into your local view?” You will then be transferred to the local view.
Notice that the retrieved map is exactly clipped as the area you had zoomed in,
and that the labeling is lost in the view in the local mode.
If you do not get the map to your local view, try
again later, the problem could be that the server is busy.
Finding
data
|
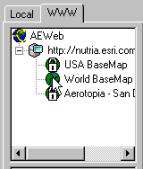
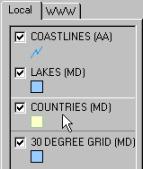
The legend should now look as the example to the
right. With the check box to the left of the label you can include or exclude
the theme from the view (try it). If you click once on the name label the
theme will become active, it appears lifted. Activate the theme COUNTRIES
(MD) as shown to the right. We will now locate Botswana (or another country)
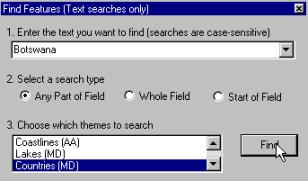
in our view by using the Find tool, |
|
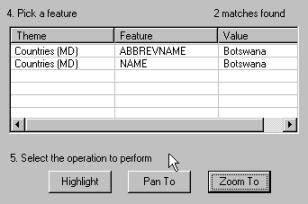
In the dialogue box that appears enter Botswana and
select the theme Countries(MD) as shown to the right. Press the Find button. The lower part of the dialogue box
will be changed as shown below. Select one of the two fields. Try all
options, Highlight, Pan To and Zoom to – in that order.
|
Notice that Botswana is a name. |
Close the find feature dialogue box.
Symbolizing data
Use the Zoom to full extent button, ![]() to get the view of the whole of Africa. As
you can see the theme coastlines (AA) also contains the borders between
countries, but that the lines do not coincide with the COUNTRIES theme. Turn of
all themes except COUNTRIES (i.e. click the check boxes to empty them).
to get the view of the whole of Africa. As
you can see the theme coastlines (AA) also contains the borders between
countries, but that the lines do not coincide with the COUNTRIES theme. Turn of
all themes except COUNTRIES (i.e. click the check boxes to empty them).
|
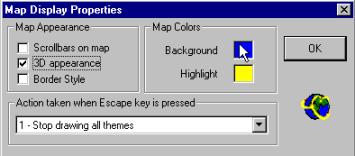
To set a background color and other map display
properties press View in the menu bar and then Map display
properties. You can add scrollbars, make the map appear 3D,
and change the color of the background (the sea in our case) and Highlight
(when you query the data the result is highlighted in this color – yellow is
default). |
|
The
next step is to symbolize and put name tags for each country.
|
Make the theme COUNTRIES active. Open the theme
properties dialogue box, either via the Theme properties button, |
|
To clear the selected/highlighted features from the
map view press ![]() Clear Selection
Clear Selection
Button. If you want to remove thematic classification from the
active theme press ![]() Clear Thematic Classification
button.
Clear Thematic Classification
button.
|
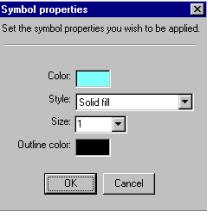
The Symbol
properties box is find in the Theme
properties box, simply click an attribute and than select Color, Style and Size. You can set individual colors, style and size
(line width) of each attribute by clicking each
attribute. In the second part of the exercise you must symbolize
European cities using this dialog box. Cities are point themes and shape,
size and color can all be changed via symbol properties. |
|
Labeling
maps
|
To label the map in ArcExplorer add a duplicate copy
of the theme countries. Use the Add theme button, |
|
Open the theme properties dialogue box for this second
countries theme – either by double clicking, through the right mouse button or
under Theme in the menu bar.
|
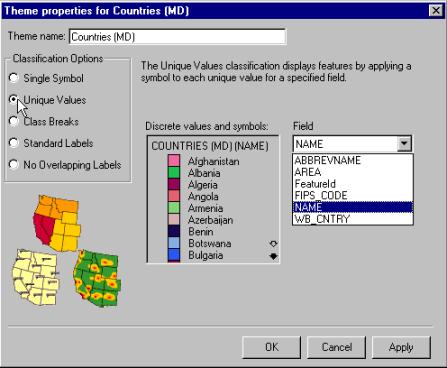
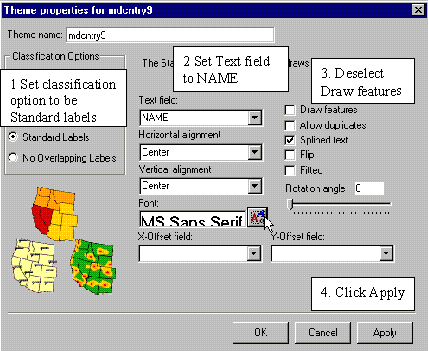
In the theme properties menu set Classification
Options to be Standard Labels. New labels and edit
boxes will appear. Select NAME as Text field and deselect Draw features. You can also change the font
if you feel like it. Press Apply and then OK. Your map should now have name labels for
countries in Africa |
|
As you will see when you display the whole African
continent the name labels are too large; it is difficult to read the names as
well as distinguish which name belongs to which country. To improve the layout
of the map you can decide a scale above or below which the name labels will not
be displayed. First zoom the map of Africa so that you can conveniently read
the labels and associate them with a particular country. Then open the theme
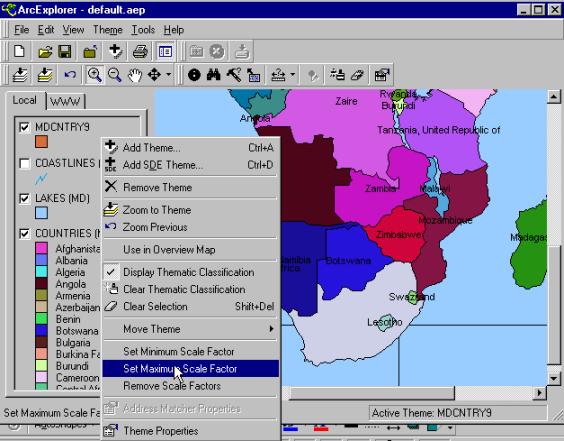
manipulator (activate the theme and press the right mouse button). Select the
option Set Maximum Scale Factor. Zoom to full extent – and voila no name
labels, if you zoom in they will reappear.
To display your view over the whole screen you can use
the Toggle
legend button, ![]() . Try
it.
. Try
it.
|
|
Zoom to full extent. If you followed the instructions
no labeling should be seen. You should now add a tool that allows you to use
the mouse for displaying selected properties of a theme. Make sure the theme
COUNTRIES is active. Click the Map tips tool, ![]() , to
display the Map Tips dialog. Select NAME in the list and click OK. When you
move the cursor in the view the name of the country where you slide the cursor
will be shown in a little box. Hands on your heart - how many African countries
do you really know?
, to
display the Map Tips dialog. Select NAME in the list and click OK. When you
move the cursor in the view the name of the country where you slide the cursor
will be shown in a little box. Hands on your heart - how many African countries
do you really know?
Set the scale and scale units
|
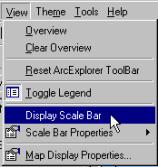
A scale bar is obligatory for a map. Thus you must
add one. This you do under View in the menu bar as shown to the right. To
change the scale bar to display kilometers and be in centimeter units change
the Scale Bar Properties (also found under View in the menu). Map
units are decimal degree so you must not change them, set Scale Units to
kilometers and Screen Units to centimeters You also need to set measure units to be able to
interactively calculate distances in the map. This is done under Tools in the menu. Set the Measure
units |
|
On the map view, click and drag a line representing
the distance you wish to measure.
Querying
data
Next we will try the Query builder, ![]() , to
see which African nations are larger than Sweden. The area of each country is
given in square miles in the theme COUNTRIES.
, to
see which African nations are larger than Sweden. The area of each country is
given in square miles in the theme COUNTRIES.
|
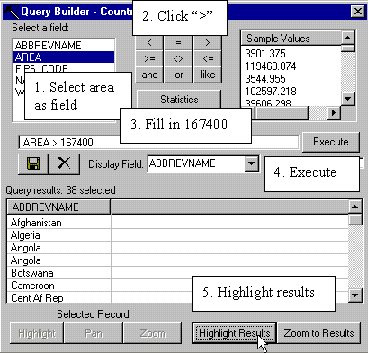
Make sure COUNTRIES is the active theme and click
the query builder. In the query dialogue box select AREA
as field
then press the “>” sign and fill in 167400 (the area of Sweden in
square miles) by hand in the query below (as to the right). Press Execute,
and then Highlight Results. Most African countries are larger than
Sweden - Africa is not a small continent. In the query builder you can also
calculate summary statistics for numerical fields. Try it out for the area of
countries. |
|
Your map of Africa should now be classified in colors
representing individual countries, and also selected according to relative size
versus Sweden. To clear the classification you can use the Clear Thematic classification tool, ![]() , and
to clear selected areas you can press the Clear selection tool,
, and
to clear selected areas you can press the Clear selection tool, ![]() . In
both cases you can also open the theme manipulator to clear thematic
classification and selection.
. In
both cases you can also open the theme manipulator to clear thematic
classification and selection.
Save the ArcView
project, ![]() ,
that you have created, preferably in your working directory. Change the name
into something logical.
,
that you have created, preferably in your working directory. Change the name
into something logical.
Add
cities over your selected country
We also want to get a theme with cities from the ESRI
site with Arc data on the www. To do this we will use another route.
|
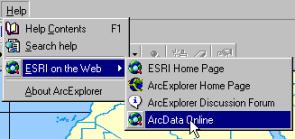
In the menu select Help and then ESRI on the Web and finally ArcData
Online as shown to the right. You will automatically be
transferred to http://www.esri.com/data/online/.
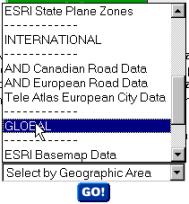
Further down on that web page open the pop up menu for Select by
Geographic Area and find GLOBAL. |
|
|
There are several alternative data sources to choose
from. Browse around among the data and have a look of some of it. The data
that we retrieved earlier were from ESRI World Reference Data Sets, and from
this set we will now retrieve global cities. Thus select ESRI World
basemap Data and “your country” (Botswana) and press the button
“Make
the map”. When the map is prepared press
Download data. Accept the license |
|
agreement and choose PC Compatible Zip as
format and Proceed to
download. Save the data to the directory where you did put the other data.
Unzip the file that you transferred.
|
If you do not have WinZip you have to download that first – for
example from http://spap.cac.washington.edu/project/wwwmm/winzip.html. |
Add the themes over your country (Botswana) that you
just retrieved to your view. Press the Add theme button, ![]() .
Navigate to the directory where you put the data. Add all the data you
retrieved (highlight them in the Add theme menu and press the Add theme in the
menu, you can also simply double click all layers).
.
Navigate to the directory where you put the data. Add all the data you
retrieved (highlight them in the Add theme menu and press the Add theme in the
menu, you can also simply double click all layers).
|
|
|
Have a look at all the data you just retrieved.
Remember: to view a theme click the check box to the left of the theme
label. To activate a theme click on the name label and the theme will appear
lifted. With the theme active you can access the theme
manipulator (shown to the right) by simply clicking the right mouse button.
Remove all themes that you have added except the three themes shown in the
above legend - AWSCITIE, AWRIV3ML1, COUNTRIES (MD). Select the COUNTRIES theme to be used as overview
map: activate COUNTRIES, click the right mouse button and select Use in
Overview Map. This map should now be seen in a small window in
the lower part of the legend as shown in the figure below. |
|
|
|
Zoom in to your selected country – a red frame in the
overview map shows the area that is displayed in the view. An alternative to
manual zooming is to activate one of the themes that only covers “your country”
and press the zoom to active themes button ![]() .
.
Retrieve
the Digital Chart of the World (DCW) from the internet
There is another www site that holds free data but with some more
details at a country level. We will use this site for mining data over land
cover, roads, hypsography (elevation), towns, lakes and rivers. DCW is a set of
maps with global coverage, and is originally actually also a product from ESRI.
DCW exists in many versions, and we will use the one available at Penn State
University (PSU). Their version exist as the ArcInfo export format *.e00 that
can be used by ArcExplorer and ArcView as well. However there are many steps
before we get a useful map. To learn more about DCW look at www.maproom.psu.edu/dcw/
When you have learnt about DCW, download the maps of your selected
study area (Botswana).
Use Internet Explorer or Netscape navigator to go to www.maproom.psu.edu/dcw from the world map that appears select the Africa
tile to work with and then ”your country” from the list that appears to the
right.
Click Africa either in the legend or the map
![]()
Digital Chart of the World
Start by viewing available themes before downloading![]()

DCW download manager
Download the following
themes:
Populated places (points)
Roads (lines)
Drainage (network)
Hypsography (network)
Land cover (polygon)
Select the layers you want to download and continue. In the DCW download manager do select [Data Compression Type] to be PC/NT and [Optional Arc View Projects] to be NONE. Then press [Compute Data]. Then just [Download Coverages]. If the downloading does not work (not uncommon) you must use a manual FTP program to download. It is important that you note the name and directory of the file that the Download Manager created for you.
|
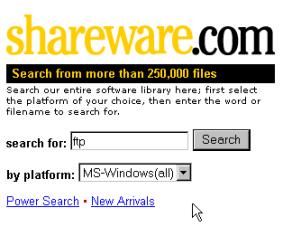
If you do not have a FTP program there is a shareware called ws ftp that you can download
from www.shareware.com. In that web
page search for ftp (as below), in the list of ftp shareware you will find ws
ftp – download this program to your hard disk. Then use WinZip to unzip ws
ftp.
|
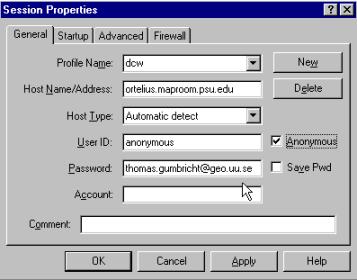
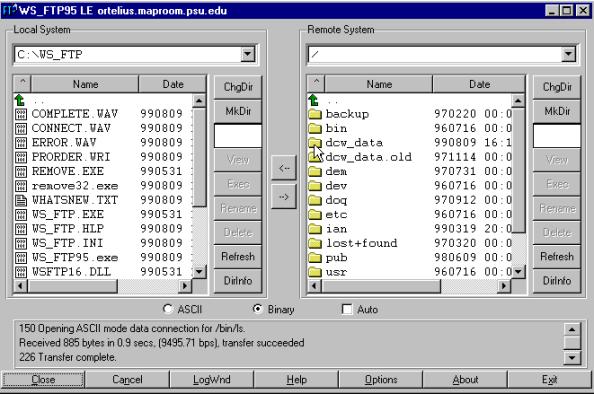
To ftp your file with DCW from PSU use the following declarations for
connecting:
|
URL |
ftp://maproom.psu.edu/dcw_data/xx (where xx is a number given to your
file by the DCW download manager) |
|
Host name |
Ortelius.maproom.psu.edu |
|
Host type |
Automatic detection |
|
User-ID |
Anonymous |
|
Password |
Anonymous or your own e-mail |
In ws ftp the declarations looks like this (where you can enter your
own e-mail as password).
|
|
Once connected to ortelius.maproom.psu.edu change remote directory to
dcw_data and then xx (where xx is the name given to you by the ftp server – see
above). Change your local directory and press transfer button, ![]() (between the two windows).
(between the two windows).
|
|
Unzip
the DCW maps and import them to ArcExplorer
The DCW files that you got from PSU are zipped, so you need to unzip
them. After unzipping you should have the following files in your directory
|
Name |
Content |
Type |
|
dnnet |
Drainage |
Coverage (arcs and polygons) |
|
hynet |
Hypsography (digital elevation model) |
Coverage (arcs and polygons) |
|
lcpoly |
Land cover |
Polygon |
|
ponet |
Political/ocean boundary (comes automatically) |
Coverage (arcs and polygons) |
|
pppoint |
Populated places (i.e. cities) |
Points |
|
rdline |
Roads |
Arcs |
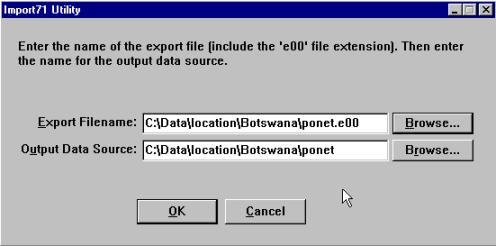
The unzipped files all have the extension *.e00, this is the export format of Arc Info, and it can be
imported to ArcExplorer or ArcView (see appendix 1). Use the program Import71
which you should have downloaded from ESRI’s homepage. As Import71 will produce
ArcInfo coverages you must put each imported theme in a separate directory.
Thus for each e00 file that you import create a directory with the same name
(as in the example below). You have to import all the maps individually.
|
|
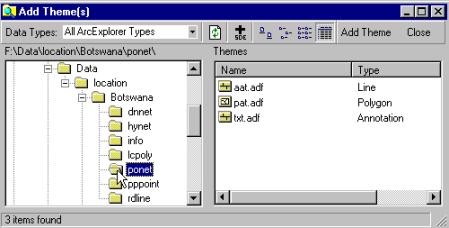
Use the Add theme tool to pick up the DCW data layers that you
imported. The DCW data that you imported from www are now stored on your local
hard disk so they should be added as local themes. In the Add theme dialogue
box navigate to the directory where you saved the files you created with
Import71. Make sure data types is eiter “All ArcExplorer Types” or “Arc/Info
Coverages”, ![]() . As
the files you got from DCW were ArcInfo coverages they usually contain more
than one theme. For example ponet (political ocean boundary) contains one theme
as polygon (a closed area showing the borders), one theme as line (a line
showing the borders) and a theme with annotations (text labels to put on the
map). Other themes might contain other types.
. As
the files you got from DCW were ArcInfo coverages they usually contain more
than one theme. For example ponet (political ocean boundary) contains one theme
as polygon (a closed area showing the borders), one theme as line (a line
showing the borders) and a theme with annotations (text labels to put on the
map). Other themes might contain other types.
|
|
Here is a suggestion on what DCW themes to add
|
Content |
Add as |
|
Political/ocean boundary |
Polygon |
|
Land Cover |
Polygon |
|
Land Cover |
Annotation |
|
Drainage |
Polygon |
|
Drainage |
Line |
|
Drainage |
Annotation |
|
Hypsography |
Line |
|
Roads |
Line |
|
Population (cities) |
Point |
|
Population (cities) |
Annotation |
The colours of the themes that you have added were set in a random
manner. Thus the next step is to set colours and classify your data. Before you
can do that you must find out what is actually shown in the different themes.
This you can do via the www site of DCW. Thus navigate to http://www.maproom.psu.edu/dcw/ and
choose ABOUT DCW.
Try to find out information about the coding of land cover, drainage
and roads. If you do not find the information here is the URL to write for
these themes:
|
Theme |
URL |
|
Land cover |
|
|
Drainage |
|
|
Road |
Once you have noted which field hold which information you can classify
and set colour to your data. This is done in the Theme properties dialogue box
which you can open by either double click the name label in the legend, or
under theme in the menu bar.
Save the ArcView
project, ![]() ,
that you have created, preferably in your working directory. Change the name
into something logical.
,
that you have created, preferably in your working directory. Change the name
into something logical.
Your turn
Having added all the data over your country it is time to create a
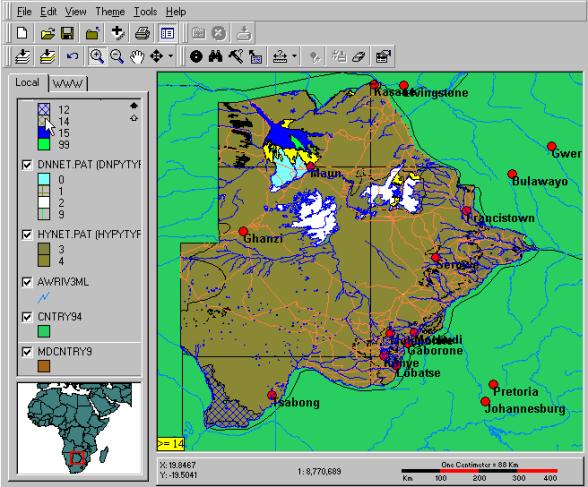
thematic map of land cover and drainage network. An example for Botswana is
shown below. The map was specifically made for illustrating the Okavango delta.
Okavango is one of Africa´s most pristine inland wetland areas, with a lot of
interesting wild life and escalating tourism. Water is a scarce resource since
the Okavango is really in the Kalahari dessert. The upstream countries Angola
and Namibia are interesting in utilising the water resources feeding Okavango
river.
The maps shown below are made from the data that you have already retrieved.
The first one is a map of the whole of Botswana showing the hydrology, the road
network and larger towns. Several more themes have their check boxes filled,
but Maximum scale is set in order not to display them at this small scale. The
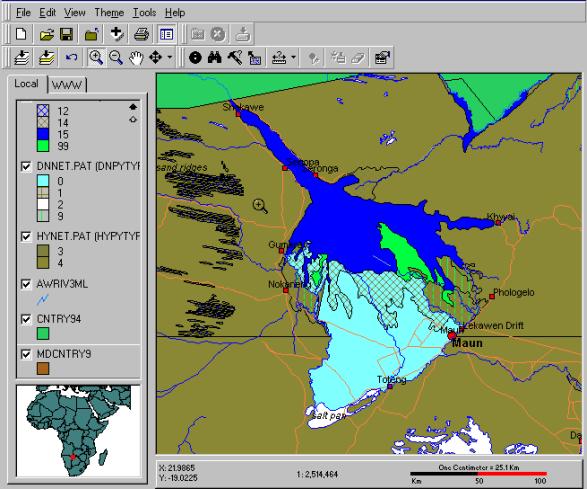
second view is a more large scale map of Okavango. Here also smaller towns and
their names are displayed. You can also see labels for major rivers and some of
the land cover. All colours for land coverage and drainage are set according to
cartographic principles. Try to create a similar map. It is not easy and you
may need to consult the manual.
|
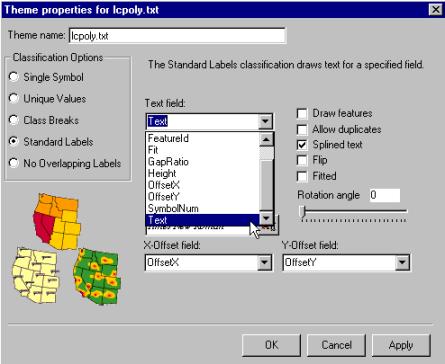
When using an Arc/Info coverage for annotation you should specify X
and Y Offset fields as shown to the right. Also remember to deselect Draw features and. Splined text means that the
text follows the form of the shape of an associated feature (useful for e.g.
rivers). |
|
Here are the thematic maps that you can use as guidance. The first map
displays the whole of Botswana. By clicking an item in a classified theme you
can highlight this theme in the map. In the example below the annually flooded
area is highlighted (indicated by the cursor – with the flooded area shown in
yellow).
|
|
Hint: An alternative way for panning in the image is to use the
overivew map.
From the larger scale map you can see some of the annotations for rivers,
smaller towns and also land cover. The white areas in the map are salt pans.
The large green part inside the delta an island.
|
|
When you are
satisfied with your cartographic product it is time to transfer it to another
media. Either print it,
|
|
To pass this exercise you must hand this map in to the course staff – either as a paper copy or in electronic format – your choice. Remember to put your name on the map.
Appendix: How to get ArcExplorer from
www
Use a web-browser (Netscape, Internet explorer) and navigate to ESRI´s
homepage (http://www.esri.com/) and to the
page with free resources, select ArcExplorer (you should then be transferred to
the site http://www.esri.com/software/arcexplorer/index.html).
Read about ArcExplorer and then press Download
ArcExplorer 1.1 in the left margin of the page (version 1.1 is the latest at the time
of writing this instruction). You should then be transferred to the page http://www.esri.com/software/arcexplorer/aedownload.html.
Close all windows applications that is
running on your PC and install ArcExplorer by running the program aeclient.exe
(the program that you downloaded). To be able to install ArcExplorer you must
have administrative rights on the computer you are using – if you do not have
that you must ask your system administrator to help you. To install and run
ArcExplorer the user should have full access (read and write) to the archive \Esri\
(not only for installation – also for running). When you install the
ArcExplorer the default path for installation is “Program files\ESRI\ArcExplorer”. It is recommended that you accept
that.
With the download you also got the manual for
ArcExplorer. It is the file called Arcexplorer.pdf,
which you can read by using Adobe Acrobat reader. If you get stuck or do not
understand a command, please refer to this document. If you do not have acrobat
reader you can download it from http://www.adobe.com/prodindex/acrobat/readstep.html.