|
Institutionen för geovetenskaper Geoinformatiklaboratoriet |
GIS Exercise 28 September 1999 |
Thomas
Gumbricht |
INTRODUCTION
TO AVENUE
FINDING
SUITABLE AREAS FOR SEISMIC STATIONS
Requirements
This exercise requires a PC with Windows 95/98 or Windows NT and the GIS software ArcView version 3.0 or later. The necessary data area available on the earth server at Geocentrum under Earth2/_sharedfiles/geoinformatik/data/... |
Objectives
This exercise will give an introduction to application development and customisation in GIS. Specifically the interface of ArcView will be customised; scripts and extensions will be added to perform specific tasks. |
Task
The result of the exercise should be a map showing suitable locations
for seismic measurement stations in Uppsala County. |
Introduction
The mid Atlantic ridge is continuously pushing North America and Europe
apart. Science can fairly well depict the large scale forces that operate,
however still predictions about specific earth quakes and volcanic activities can
not be done with any significant accuracy. In order to improve the
understanding of the forces generating earth-quakes and volcanic activity
several countries have joined forces. A new net of measuring stations for
seismic activity is thus going to be set up. In Sweden 8 to 10 stations are to
be set up along the Baltic coast from Uppsala to Haparanda. The localisation of
a seismic measuring station is sensitive - no sources giving rise to vibration
in the bedrock are allowed in the neighbourhood. The internal geometry of the
stations is also important - the perfect geometry is to have a station at each
intersection of a set of regular triangles. Sources of disturbance include
lakes and the sea, traffic and communications systems, power stations and power
lines, military shooting and training fields, and built up areas (see below).
All major source factors can be found in Röda Kartan - the 1:250 000 scale map
produced by the Swedish Survey, normally published per county. Apart from
identifying disturbance sources, the seismic stations must of course be placed
in solid rock. Thus only areas with barren rock or thin soil are suitable. The
Swedish Geological Survey has published a national soil map of Sweden in the
scale 1: 1 million that shows such areas. In this exercise you shall add
modules and customise ArcView so that it can solve the problem of localising
potential areas suitable for seismic measuring stations. Uppsala County will be
used as an example.
Introduction to customisation and programming in ArcView
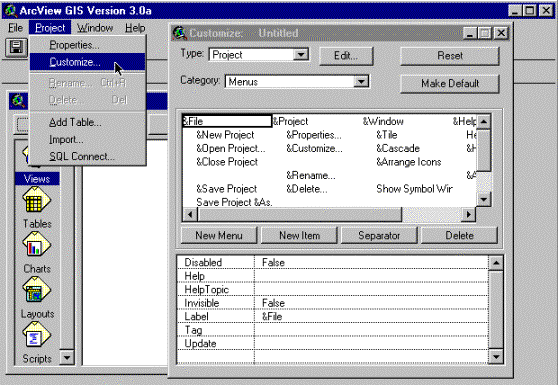
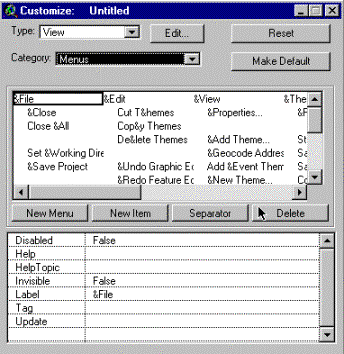
Start ArcView and open an empty view. Under Project in the menu select Customize, the following menu appears.
|
3. In the lower window the properties
of each item are defined. 2. The upper window shows all items
(menus, buttons and tools) associated with the document windows. 1. Select Project in the menu and then Customize in the drop down menu. |
With the Customize dialogue box you can change the menu bar, buttons
and tools of ArcView. You can also add new buttons or tools.
Each menu item, button and tool in ArcView is associated with a script. A script is a program written in
ArcView’s development language Avenue.
Everything you do in ArcView is run by scripts. The set of scripts that ArcView
uses as default are called system scripts.
ArcView is however delivered with several more scripts that you can load to the
system yourself - these are found under
C:\esri\av_gis30\arcview\samples\scripts. Another important source for scripts
is ESRI´s www site (http://www.esri.com/).
And then it is also possible to write your own script in Avenue.
|
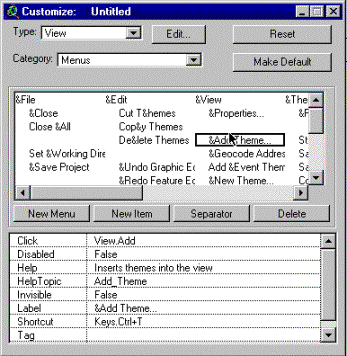
4. Note the definitions of the Add
Theme item in the View menu 3. Point with mouse to &Add Theme… 2. Change Category to Menu 1. Change Type to View |
|
Do not make any changes in the customize dialogue menu - instead just
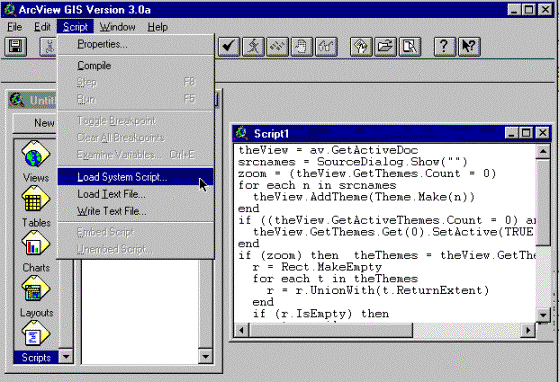
close it and return to your project window. In the project window select Script and press New. From the menu do select Script and Load System Script as shown below.
In the Script manager box that appears go down to the script View.add and add it. You can now read
the Avenue program text of the script View.add.
If you are familiar with programming you will recognise some features, like
conditional statements (if .. then) and loops (for each ….).
|
|
Close the script.
Finding suitable areas for seismic measurement stations
Let us turn to the task of creating a customisation that can be used to
seek out areas suitable for seismic measuring stations along the Swedish Baltic
coast north of Stockholm. The first part in creating the customisation is to
define what needs to be done.
|
Operation that will be needed |
Arc View equivalent |
|
Add necessary themes over the county |
Add Theme |
|
Delete themes (not obligatory, but might be useful) |
Delete theme |
|
Query features of a theme to be used separately |
Query builder |
|
Clip the theme ”Soil map of Sweden” to fit the county |
Clip theme |
|
Evaluate proximity from different themes and features |
Proximity analysis |
|
Zoom tools |
Zoom in, Zoom out, pan, Zoom to full, Zoom to selected |
|
Definition of view properties (map and distance units) |
View properties |
Even though the task of identifying undisturbed areas with rock
outcrops is rather difficult it only involves a few generic steps. Most steps
can be done by ArcView system scripts. Clipping themes must, however, be done
by a script supplied with the ArcView license that you must add yourself,
whereas the script that evaluates proximity can only be found at ESRI’s www
site.
Customisation
of the interface of the View document
Return to the project window and open a new empty view. To activate the
customisation dialogue box from the view document you can double click on the empty
area to the right of the tools.
|
Double click in the empty space to
activate customisation |
|
You will again get the Customize dialogue menu - this time defaulted
to Type being View (as shown to
the right). Do not press
the button Make default (if you do we will have to reinstall ArcView on that
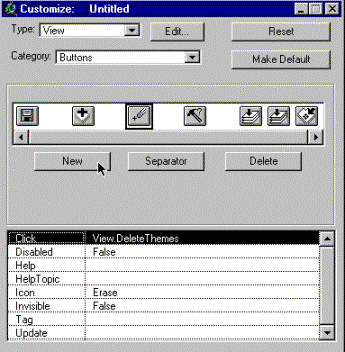
computer later). The first thing to do is to delete the menu item, buttons
and tools that are superfluous. To delete an item just press the Delete button between the two windows of the dialogue box. The item inside
the box in the upper window will be deleted. As you delete something the
corresponding menu item, button or tool disappears. Be careful not to delete
too much. Here is a suggestion on what to keep.
|
|
In the example above three menus, seven buttons, and six tools have
been kept. We also want to have possibilities to delete files. In the original
interface that is a menu option, however we will put it as a button in our
customisation.
|
3.Define the properties of the New
button 2. Insert a New button 1. Insert a blank by pressing
separator |
|
The name is again a logical outcome of object orientation. The object
we want to change is the view, the request we send to that object is to delete
a theme. Obviously no other object have the possibility of deleting a theme. In
object oriented programming requests and objects go hand in hand.
Add the necessary data
Before continuing it is time to add the themes that we need in order to complete our task. As said above all the features we want to analyse proximity from can be found in the themes of Röda Kartan (all themes are under the directory Earth2/_sharedfiles/geoinformatik/data/clan).
|
Disturbance feature |
Röda Kartan layer |
kkod |
Disturbance distance (m) |
|
Railroad (various types) |
rc_jv95 |
5611 - 5632 |
5000 |
|
Military exercise field |
rc_mo95 |
432 |
5000 |
|
Military shooting field |
rc_ms95 |
4310 |
5000 |
|
Military protected area |
rc_my95 |
433 |
5000 |
|
Nuclear power plant |
rc_sp95 |
362 |
5000 |
|
Mine |
rc_sp95 |
321 |
5000 |
|
Coast line (mainland) |
rc_hv95 (rc_ku95) |
9000, 9009 |
3000 |
|
Built up areas |
rc_to95 |
302, 303 |
3000 |
|
Major roads |
rc_av95 |
5011 - 5321 |
2000 |
|
Airport, > 1200 meters |
rc_sl95 |
5710 |
2000 |
|
Airport, other |
rc_sp95 |
571 |
1000 |
|
Helicopter landing place |
rc_sp95 |
572 |
1000 |
|
Wind power |
rc_sp95 |
361 |
1000 |
|
Chimney |
rc_sp95 |
326 |
800 |
|
Tower |
rc_sp95 |
322 |
800 |
|
Radio mast |
rc_sp95 |
323 |
800 |
|
Church |
rc_sp95 |
351, 352 |
800 |
|
Power line (various types) |
rc_kr95 |
4510, 4520 |
300 |
|
Lakes (> 1 km2) |
rc_sj95 |
901 |
200 |
Apart from the layers of Röda kartan in the list above there are two
more themes you must add - the soil map covering Uppsala county - jordclan; and the theme showing the
county itself - rc_ln97. These files
are also found in the Rodakartan directory.
Once the Themes are loaded set the map and distance units in the View
properties (or else no distances can be calculated).
Clip the Soil map theme to fit the county
The soil map (jordclan) that
you loaded is part of the national soil map produced by SGU (Swedish Geological
Survey) in the scale 1: 1 million. As you can see, however, its extensions do
not match that of the other maps of Uppsala county that you have loaded. In
order to save storage space and improve the cartographic layout you should now
clip the soil map to fit the county. There is no system script doing this.
There is however a script doing exactly what we want supplied with the ArcView
program. It is called ClipThm.ave
(all scripts have the default extension .ave). You can find it together with
all other scripts supplied with the program package under
C:\esri\av_gis30\arcview\samples\scripts.
The script ClipThm.ave is
only needed once and we will run it as a script document instead of associated
with a menu, button or tool item. Go to the project window, select script as
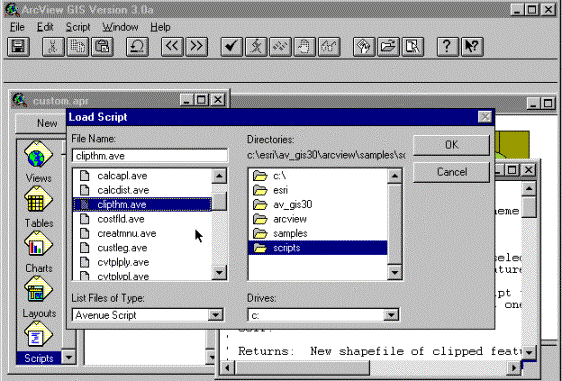
document type and press New. You will get an empty script. Choose Script in the menu and then Load Text File in the drop down menu. In
the dialogue box that appears navigate to C:\esri\av_gis30\arcview\samples\scripts
and select the script ClipThm (see
below).
|
4. Navigate to C:\esri\av_gis30\
arcview\Samples\scripts and add the script clipthm.ave 2. Press New to create an empty
script. 3. Choose Script and Load Text File in the drop down menu. 1. Choose script as document type. |
As with all computer programs before executing it you must compile it.
You compile a script with the compile button ![]() . Note that the
run button,
. Note that the
run button, ![]() , to the right of
the compile button became enabled when you compiled the program. Run the
program. Most likely you will encounter an error. That is because the script
does not recognise the view document. Thus activate the view with your themes,
then activate the script (activate by clicking on the bar above the document -
the bar that turns blue when active). If you go directly from the View to the
Script, the latter will interpret the former as active. Again run the program
and set ”intersect” theme to be the soil map and ”clipping” theme to be the map
that shows the extension of your county. Save the county soil map in your
working directory and add it to your View. If it worked out OK you can delete
the original soil map.
, to the right of
the compile button became enabled when you compiled the program. Run the
program. Most likely you will encounter an error. That is because the script
does not recognise the view document. Thus activate the view with your themes,
then activate the script (activate by clicking on the bar above the document -
the bar that turns blue when active). If you go directly from the View to the
Script, the latter will interpret the former as active. Again run the program
and set ”intersect” theme to be the soil map and ”clipping” theme to be the map
that shows the extension of your county. Save the county soil map in your
working directory and add it to your View. If it worked out OK you can delete
the original soil map.
Creating buffers around the disturbance sources
There is neither a system script nor another supplied script that does
calculate proximity and saves the results. However, as said above on ESRI´s
internet site several more scripts donated by ArcView users can be found and
downloaded. Use your internet browser and navigate to http://www.esri.com/. On the main ESRI page you
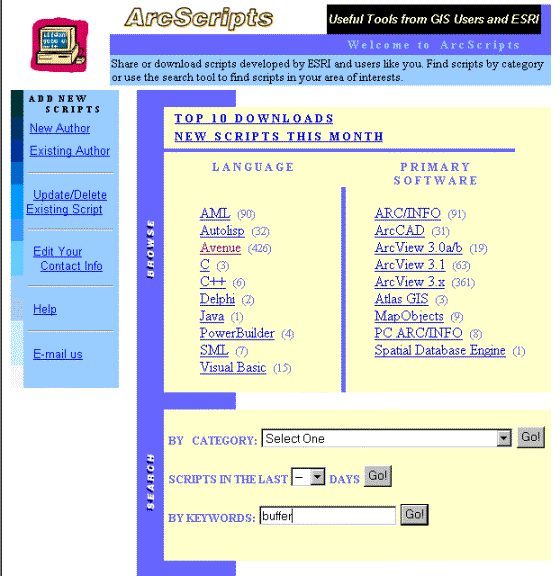
can find your way to the scripts in the left margin, or use the address http://andes.esri.com/arcscripts/scripts.cfm.
As you will see from the script page (cf. below) there are quite a lot
of scripts to download (however the list also include all the sample scripts
delivered with ArcView). Use the search function as indicated below to find
scripts that create buffers.
|
Type ”buffer” and then search by
pressing ”Go” |
The script you must use is Buffer Theme Manager (1a) by Kevin O'Malley.
Follow the instructions and download the zip file which contains the script to
your working directory. Unzip the file that you downloaded. The zip file
contain four files:
|
avdlog.dat |
|
|
avdlog.dll |
|
|
buffread.txt |
|
|
buffthme.avx |
|
If you do not have Winzip on the computer you are using, download a
demo version from the internet – e.g. from the site http://www.winzip.com/downhome.htm.
If you have limited rights on the computer you are using put winzip in the temp
directory and also install winzip under the temp directory.
Before continuing read the instructions in the file buffread.txt. From the instructions it should be clear that you
need to copy the files as follows:
|
File |
Copy to |
|
avdlog.dat |
C:\ESRI\AV_GIS30\ARCVIEW\LIB32 |
|
avdlog.dll |
C:\ESRI\AV_GIS30\ARCVIEW\BIN32 |
|
buffthme.avx |
C:\ESRI\AV_GIS30\ARCVIEW\EXT32 |
|
Buffthme.avx was created as
an avenue script, however, it was saved as an extension instead of a script -
hence the .avx instead of .ave. Extensions are modules that can be loaded to
ArcView. When an extension is loaded the interface of one or several
documents (views, tables, charts, layouts and scripts) are affected - menu
items, buttons and tools are added. All extensions must be located in the
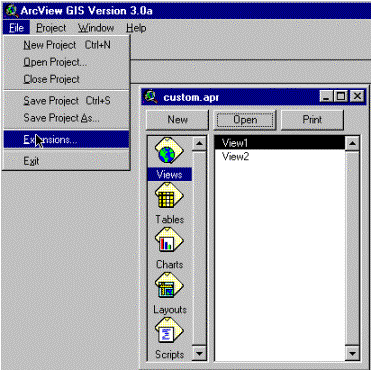
directory C:\esri\av_gis30\arcview\ ext32, where you just did put the buffer extension. To load the
extension go to the project window, choose File and Extensions. |
|
|
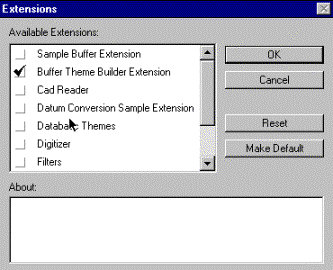
In the extensions dialogue box you will see the extensions available
(i.e. files ending .avx in the directory ..\ext32). ArcView is delivered with
several extensions (Cad Reader, Data Base Themes etc). You will also see the
extension ”Buffer Theme Builder Extension” which is the one you downloaded
from the internet. Click in the box to the left of the extension to activate
it. Return to the your view. It should now have an extra button for creating
buffer themes - |
|
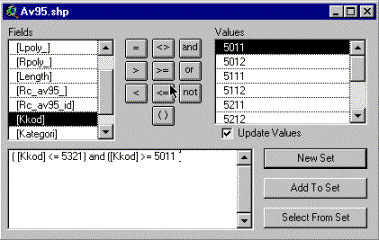
Obviously some of the themes as they are defined in Röda Kartan do not
match the definitions as we want to use them. So we must use query to select
the various sets of features we want to use for doing our proximity analysis.
|
To the right you can see how the query function is used to select all
the major roads (as defined above) from the theme containing all public
roads. If you do not select any road the buffering will be around all public
roads - meaning that most of the county will be constrained (or closed) for
localising a seismic measuring station. |
|
|
For each of the disturbance features identified above you have to run
the Create Buffer Theme tool. Before running the
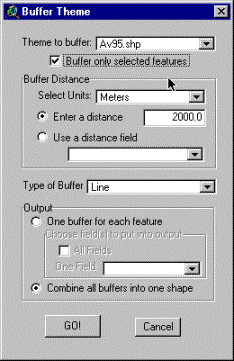
tool you must select the features of the specific theme. To the right is an
example of running the tool for the theme av (public roads) with selected features being ”Major roads”. The
distance is calculated only from selected features; the distance is set to
2000 meters; no distance field is used; Type of Buffer is set to the same
feature as the theme; and all buffers are combined into one shape. Use the
same principles for deriving all buffers. |
|
|
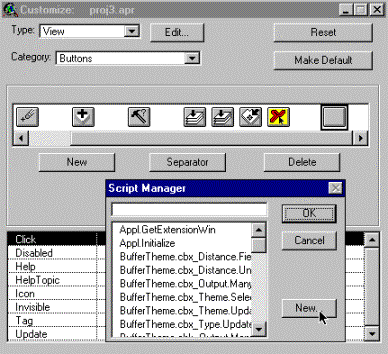
3. Create a new script 2. Active the Click property 1. Add a new button Open the Customize dialogue box, and add a new button as shown to the
right. Go down to the line with the Click property and double click. You will
recognise the list of system scripts. However, there is no system script
available, thus press New. |
|
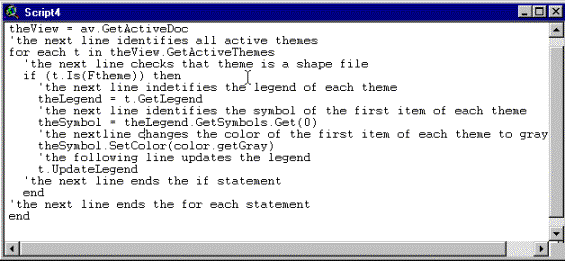
The script window that appears has one line of code:
theView =
av.GetActiveDoc
theView is a variable
that is assigned the value av.GetActiveDoc. The object av is the only instance of the
active document class (there can only be one instance of av in each active
application). The meaning of the other lines are given below, the ´ sign
denotes a comment line. Write the code into your scrip, compile it and try to
run it. The script will change the colour of all active themes to grey.
|
|
When you have calculated all the buffers and set all the colours you
are ready to create a layout. The map shall give information on where barren
rock can be found in Uppsala County outside the disturbance buffer zones. This
map must be handed in to the course staff to pass the exercise. You can send in
the map in digital or paper format. Do not forget to write your full names on
the map you hand in.